| |
|
|
Structural lightning protection design considerations |
|
BS 6651 (Protection of structures against lightning) clearly advises strict adherence to the provision of a conventional Lightning Protection System (LPS) to the total exclusion of any other device or system for which claims of enhanced protection are made. Principle components of a conventional structural lightning protection system, in accordance with BS 6651 are:
| |
| Air termination network | |
| On high risk structures such as explosive factories, no part of the roof should be more than 2.5m from an air termination conductor. This is generally achieved by applying a 5m x 10m mesh to the roof. However, for most structures, a mesh of 10m x 20m is considered sufficient, giving a maximum distance from any part of the roof to the nearest conductor of 5m. |
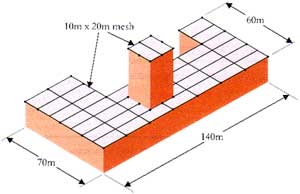 |
This
involves rolling an imaginary sphere of 60m radius over a structure.
The areas touched by the sphere are deemed to require protection. On
tall structures, this can obviously include the sides of the building. | |
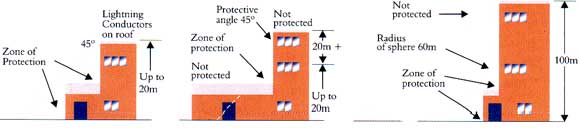 |
|
| |